-
Embryo-Engineered Nonhuman Primate Models: Progress and Gap to Translational Medicine
2021-09-24
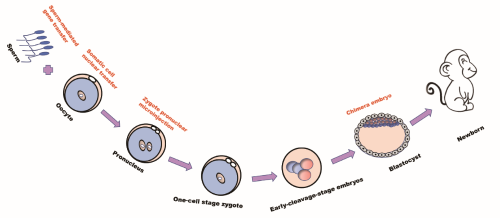
Nonhuman primates (NHPs) are better models for human disease because of their high similarity to human beings in genome, brain structure, advanced cognitive function, immune and metabolic systems. In recent decades, many types of NHP disease models have been created through embryo engineering base approach (Figure 1), which often combined with other genetic and cell engineering. Fortunately, most of the reported NHP models well simulate the characteristics of the occurrence and development of human diseases. This means the NHP disease models are helpful to better understand disease pathogenesis and develop new therapeutic strategies.
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of genetically modified animal models using embryo engineering.
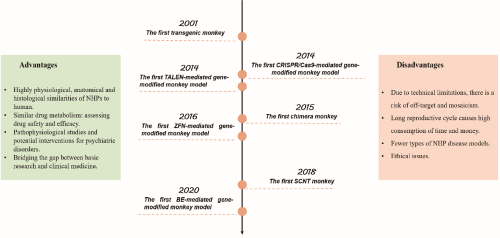
Professor Yongchang Chen’s group from the Kunming University of Science and Technology focuses the research on modeling diseases of the human nervous system. They recently published a review paper that summarized the key progress of NHP models generated by embryo engineering, analyzed their unique advantages in mimicking clinical patients, and discussed the remaining gap between basic research of NHP models to translational medicine (Figure 2). Since the first retrovirus-mediated transgenic monkeys, scientists have created several kinds of monkey models of nervous system diseases, such as Huntington’s disease (HD), Parkinson’s syndrome (PD) and autism spectrum disorders (ASD). In 2014, the first monkey model based CRISPR/Cas9 was constructed successfully. By this technology, Duchenne muscular dystrophy syndrome (DMD), perinatal lethal syndrome, autism spectrum disorder (ASD), adult polycystic Renal (ADPKD) and other precise gene knockout NHPs disease models have been constructed subsequently. In 2018, the successful application of somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT) technology in NHPs is undoubtedly a breakthrough. The base editors (BE) technology also be achieved in NHPs in 2020, and Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome (HGPS) monkey model was successfully obtained by BE approach.
https://spj.sciencemag.org/journals/research/2021/9898769/
Above NHPs model display great advantages in better mimic clinical patients. However, there are still several shortcomings, such as the occurrence of mosaicism and off-target, insufficient number of models, high cost, and long experimental period (Figure 2). Nevertheless, the high similarity between NHPs and humans in all aspects allows them to better simulate human diseases, find better disease treatment strategies for patients, and promote the transformation of basic research into clinical practice. In short, this review has made a comprehensive summary and analysis of the progress, opportunities and challenges about NHPs embryo engineering models, and hope to have a reference for the development of this field.
Figure 2. Major breakthroughs of the NHPs models and their advantages and disadvantages.
Tag: Health science
Source: https://spj.sciencemag.org/journals/research/2021/9898769/