-
Highly Robust and Wearable Facial Expression Recognition via Deep-Learning-Assisted, Soft Epidermal Electronics
2021-08-27
The facial expressions are a mirror of the elusive emotion hidden in mind and thus capturing expressions is a crucial way of merging inward world and virtual world. Human beings convey their emotional status and intentions mainly via facial expression, which contains rich emotional and cognitive information and is of practical importance in sociable robotics, medical treatment, driver fatigue surveillance, especially human-computer interaction. However, typical facial expression recognition (FER) systems are restricted by environments where the faces must be clearly seen for computer vision, or rigid devices that are not suitable for the time-dynamics, curvilinear face.
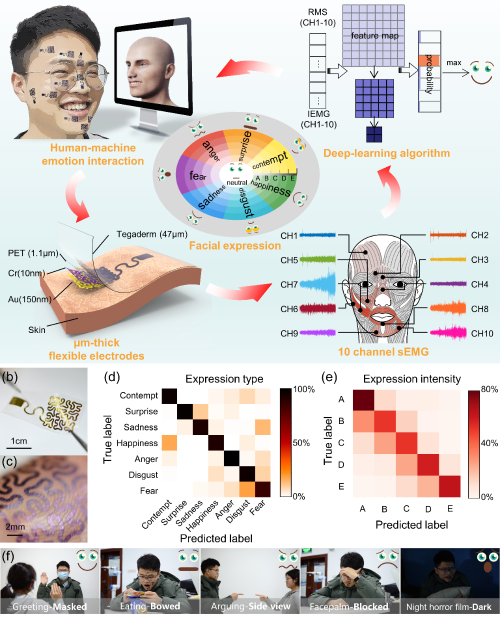
Professor Huang Yongan of Huazhong University of Science and Capital Normal University present a robust, highly wearable FER system which is based on deep-learning-asisted, soft epidermal electronics. The wearable epidermal electronics can capture subtle facial EMGs, which is naturally robust to pose, occlusion and lighting variations in different environments. The experimental results show that the flexible electrodes will not be damaged despite the plastic deformation when the face undergoes super deformation. These soft, stretchable flexible electrodes have a more reliable contact interface with human skin than commercial gel electrodes.
In addition, this study used data preprocessing and deep learning intelligent algorithm, experimental results show that the method can significantly improve both the recognition accuracy of facial expression type and intensity based on small samples. The proposed system is based on ground-truth action unit (AU) to obtain AU measurement and it avoids accurate AU annotation which requires expertise knowledge. The novelty of capturing AUs and intensity will provide new method for facial expression database construction. The combination of data pre-processing and deep learning suppresses differences of batches and individuals. Thanks to the combination of ultra-thin flexible electrodes and intelligent algorithms, the accuracy of classification in 7 expression types and intensities reaches up to 94.48%, 92.51%, respectively.
Figure 1 Overview of the wearable FER system.
The flexible electrodes do not hinder spontaneous expressions and can be worn for a week-long time. Since AUs are controlled by facial muscles, the electrodes are designed to capture subtle muscle movement corresponding to the specific AUs which are crucial to emotion understanding. It is the first time to use epidermal electronics with AUs for FER. The novelty of capturing AUs and intensity will contribute to new facial expression database construction method. The combination of data pre-processing and deep learning suppresses differences of batches and individuals. In further research, if the amount of training data is expanded, the accuracy will be improved. High-accuracy FER was accomplished in different scenarios such as illumination changing, side view, and occlusion.
This wearable facial expression recognition system has high robustness and accuracy, which is more suitable for daily life of individuals. Wearable skin electronic devices can capture subtle facial EMG signals. It is a completely different but complementary facial expression recognition strategy to computer vision, which is applicable to multi-person fixed scenes. This method is complementary to the computer vision-based method. Experiments on human-avatar emotion interaction and language disambiguation were carried out, demonstrating the application prospect of the FER system in human-computer interaction and aiding verbal communication. Further research may focus on a system-level integration, and sEMG can also be used as a complement to visual or verbal signals, combining their respective features and advantages with being of more value in multimodal human-computer interaction.
Tag:Information Science
Source: https://spj.sciencemag.org/journals/research/2021/9759601/